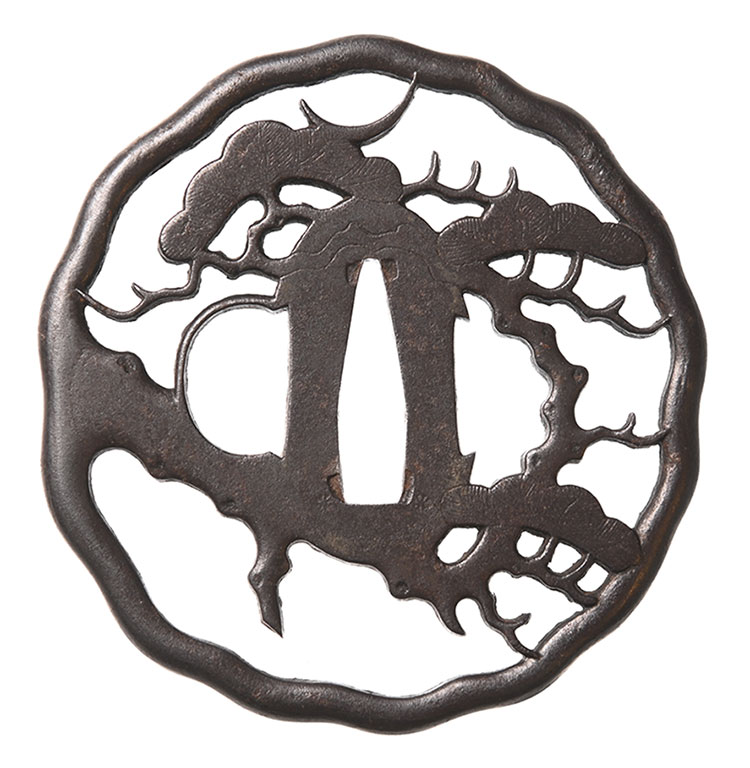
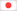
保存刀装具 Hozon Tousougu
赤坂鍔Akasaka Tsuba
No.876033赤坂 月下松樹透Akasaka Gekka Syouju(moonlight pine tree)-sukashi
- 極めKiwame
- 赤坂Akasaka
- 法量Size
-
縦 8.4cm 横 8.0cm 切羽台 0.6cm 重量 114.0g
Length 8.4cm Width 8.0cm Seppadai 0.6cm Weight 114.0g
- 国Country
- 武蔵Musashi
- 説明Drscription
- 変わり形 鉄地 肉彫地透 丸耳
赤坂派は初代・二代の忠正親子が江戸へ寛永頃移住し、尾張透の手法と京透の工法に工夫を加えて鐔を制作し、幕末頃まで栄えた。初・二・三代(古赤坂)は、鉄地の鍛が良好で造形は丸形、丸耳で厚手のものが多く、角丸風造りも見られる。四代目忠時の頃から鐔もやや薄くなり、精巧な造込となった。赤坂という呼称はこの一門の職人たちの居住地(現在の東京都港区の赤坂一帯)から用いられた。Kawarigata Tetsuji Nikuborijisukashi Marumimi
The first and second generations of the Akasaka school, Tadamasa Tadamasa, moved to Edo around the Kan'ei era, where they produced tsuba by adding ingenuity to the Owari Toru method and the Kyoto method, and prospered until the end of the Edo period. The 1st, 2nd and 3rd generation (Ko-Akasaka) have good forging of the iron base, and many of them are round and thick with round ears. From around the time of Tadatsuki IV, the tsuba became a little thinner and became more elaborately crafted. The name Akasaka was used from the place where the craftsmen of this family lived (present-day Akasaka area in Minato Ward, Tokyo).